Physics for engineer/Motion
Motion is cause by a force interacts with matter to make matter move from one place to another place . Strength to kick a ball to move from place A to place B
Chracteristics of motion
Velocity
Speed indicates the speed of motion to travel a distance over time
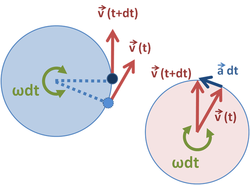
Acceleration
Acceleration indicates the change of speed of motion
Distance
Distance indicates the length of travel path of motion
Force
A physcial quantity intaeracts with matter to perform a task
Work
Work indicates the capability of a force to perform a task
Energy
Energy indicates the capability of a force to perform a task over time
Formula
Tính Chất Ký Hiệu Công thức Time Acceleration Speed Distance Force Work Energy
Types of Motion
Linear Motion
Linear Motion represents motion that follows straight line without changing its direction
Accelerationn of linear motion passes through 2 points
From above
Speed of linear motion
Distance of linear motion
Fromm above
Linear Motion with acceleration not equal zero
Linear Motion with acceleration equal zero
Linear Motion with acceleration equal constant
Curve Motion
Continous motion
Average acceleration for curve motion
Average distance for curve motion
As
Instantanous acceleration for curve motion
Instantanous distance for curve motion
Bounded continous motion
Distance for curve motion from A to B
Circular Motion
Full circle
Arc of circle
Oscillation
Horizontal Oscillation
Oscillation of spring in the horizontal direction
Vertical Oscillation
Oscillation of spring in the vertical direction

Inclined Oscillation
Oscillation of pendulum in the titlted direction
Wave
From above, oscillation generates sin wave that process wave equation and wave function
Wave equation and wave function
Wave form
Wave equation
Wave function
Formula of motions
Moment
v < C
Tính Chất Ký Hiệu Công thức Time Speed Acceleration Distance Force Work Energy Moment
v = C
Tính Chất Ký Hiệu Công thức Time Speed Acceleration Distance Force Work Energy Moment
v > C
Tính Chất Ký Hiệu Công thức Time Speed Acceleration Distance Force Work Energy Moment
Linear motion
Inclined Linear motion
Tính Chất Ký Hiệu Công thức Time Acceleration Speed Distance Force Work Energy
Vertical Linear motion
Tính Chất Ký Hiệu Công thức Time Acceleration Speed Distance Force Work Energy
Horizontal Linear motion
Tính Chất Ký Hiệu Công thức Time Acceleration Speed Distance Force Work Energy
Curve motion
v(t) =
Tính Chất Ký hiệu Công thức Distance Time Speed Acceleration Force Work Energy
s(t) =
Tính Chất Ký hiệu Công thức Time Distance Speed Acceleration Force Work Energy
Circular motion
Full circle motion
Tính Chất Ký Hiệu Công thức Time Distance Speed Acceleration Force Work Energy
Circular Arc motion
Tính Chất Ký Hiệu Công thức Time Distance Speed Acceleration Force Work Energy
Oscillation motion
Horizontal Osicllation
Vertical Osicllation
Inclined Osicllation
Wave motion
Wave function
Wave equation
Tính Chất Ký Hiệu Công thức Time Distance Speed Acceleration Force Work Energy
Force and Motion
From Newton laws
- Force equals zero . Matter is stationary
- Force is not zero . Matter is in motion
- Sum of the forces equal zero . Matter is in equilibrium
Force of momentum travels horizontaly
Force of momentum travels verticaly
- O
- |
- V
Equilibrium for hang in the air
- Fp > Fg Matter stays above
- Fp < Fg Matter stays below
- Fp = Fg Matter stays hang in the air